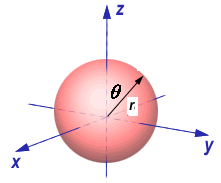
y = r sin(q) sin(f),
z = r cos(q).
The Y atomic orbitals of hydrogen like (one electron) atoms and ions in 3D space
Cartesian coordinates expressed with spherical coordinates :
 |
x = r sin(q) cos(f), y = r sin(q) sin(f), z = r cos(q). |
Separation of the coordinates: .
Radial part of Y(r,q,f): Rn,l(r) (it depends on two quantum numbers n and l; it is a real function),
Angular part of Y(r,q,f): Yl,m(q,f) (it depends on two quantum numbers l and m; it can be a real or complex function).
Y(r,q,f) = Rn,l(r).Yl,m(q,f)
The r is expressed in atomic distance unit (bohr). Conversion to SI units: 1 bohr = 52.918 pm. Generalization for arbitrary Z atomic number: replace the r by r.Z in Rn,l(r), and multiply by Z(3/2+l).
|
Quantum numbers |
Atomic orbital |
Radial part |
Angular Yl,m(q,f) |
R2n,l(r) | 4pr2Y2(r) | |||
n |
l |
m |
real |
complex | ||||
1 |
0 |
0 |
|
4e-2r | ||||
2 |
0 |
0 |
|
|||||
2 |
1 |
0 |
|
|||||
2 |
1 |
(±1) |
|
e±if | ||||
3 |
0 |
0 |
|
|||||
3 |
1 |
0 |
|
|||||
3 |
1 |
(±1) |
|
e±if | ||||
3 |
2 |
0 |
|
|||||
3 |
2 |
(±1) |
|
e±if | ||||
3 |
2 |
(±2) |
|
e±2if | ||||
4 |
0 |
0 |
|
|||||
4 |
1 |
0 |
|
|||||
4 |
1 |
(±1) |
|
e±if | ||||
4 |
2 |
0 |
|
|||||
4 |
2 |
(±1) |
|
e±if | ||||
4 |
2 |
(±2) |
|
e±2if | ||||
4 |
3 | 0 | 4fz3 |
|||||
Copyright Csonka Gábor István, BME